Mrs. King - School Year 2010-2011
Friday, June 12, 2020
Thursday, June 11, 2020
HOW TO BOOST UP BROWSING SPEED?
Internet speed is the most cared factor when you buy an internet connection. What if still, you face a slow speed browsing problem? No worries, as I came with a solution to this problem. I will let you know how to boost up browsing speed. It's very simple to follow.
SO, HOW TO BOOST UP BROWSING SPEED?
There can be many ways you can get a speedy browsing whether you use paid service or free hacks. I am going to share this free speed hack with you.
STEPS TO FOLLOW
- Navigate to Control Panel > Network and Internet Options > Network and Sharing Center.
- Now look for the active internet connection to which you're currently connected to.
- Open up Connection Properties of your active connection.
- Click on IPv4 and open its Properties.
- Here you will notice your DNS, you just need to change your DNS address with the following DNS.
Preferred DNS server: 208.67.222.222
Alternate DNS server: 208.67.220.220 - Once done, save it and no configure it for IPv6. Just change the IPv6 DNS with the following DNS.
Preferred DNS server: 2620:0:ccc::2
Alternate DNS server: 2620:0:CCD::2 - Finally, save and you're done with it.
That's all. You have successfully learned how to boost up browsing speed. Hope it will work for you. Enjoy speedy internet..!
More articles
BurpSuite Introduction & Installation
What is BurpSuite?
Burp Suite is a Java based Web Penetration Testing framework. It has become an industry standard suite of tools used by information security professionals. Burp Suite helps you identify vulnerabilities and verify attack vectors that are affecting web applications. Because of its popularity and breadth as well as depth of features, we have created this useful page as a collection of Burp Suite knowledge and information.
In its simplest form, Burp Suite can be classified as an Interception Proxy. While browsing their target application, a penetration tester can configure their internet browser to route traffic through the Burp Suite proxy server. Burp Suite then acts as a (sort of) Man In The Middle by capturing and analyzing each request to and from the target web application so that they can be analyzed.
Everyone has their favorite security tools, but when it comes to mobile and web applications I've always found myself looking BurpSuite . It always seems to have everything I need and for folks just getting started with web application testing it can be a challenge putting all of the pieces together. I'm just going to go through the installation to paint a good picture of how to get it up quickly.
BurpSuite is freely available with everything you need to get started and when you're ready to cut the leash, the professional version has some handy tools that can make the whole process a little bit easier. I'll also go through how to install FoxyProxy which makes it much easier to change your proxy setup, but we'll get into that a little later.
Requirements and assumptions:
Mozilla Firefox 3.1 or Later Knowledge of Firefox Add-ons and installation The Java Runtime Environment installed
Download BurpSuite from http://portswigger.net/burp/download.htmland make a note of where you save it.
on for Firefox from https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/foxyproxy-standard/
If this is your first time running the JAR file, it may take a minute or two to load, so be patient and wait.
Video for setup and installation.
You need to install compatible version of java , So that you can run BurpSuite.
- Pentest Hardware
- Pentest Owasp Top 10
- Pentest Windows
- Hacking Browser
- Pentester Academy
- Hacking Websites
- Pentestmonkey Sql Injection
- Pentest Active Directory
- Hacking The Art Of Exploitation
- Pentest Documentation
- Pentestmonkey
- Hacking Lab
- Pentest Stages
- Hacking Growth
- How To Pentest A Network
- Pentest Basics
- Pentest Tools Free
- Hacking Box
- Hacking 3Ds
Printer Security
Printers belong arguably to the most common devices we use. They are available in every household, office, company, governmental, medical, or education institution.
From a security point of view, these machines are quite interesting since they are located in internal networks and have direct access to sensitive information like confidential reports, contracts or patient recipes.
TL;DR: In this blog post we give an overview of attack scenarios based on network printers, and show the possibilities of an attacker who has access to a vulnerable printer. We present our evaluation of 20 different printer models and show that each of these is vulnerable to multiple attacks. We release an open-source tool that supported our analysis: PRinter Exploitation Toolkit (PRET) https://github.com/RUB-NDS/PRET
Full results are available in the master thesis of Jens Müller and our paper.
Furthermore, we have set up a wiki (http://hacking-printers.net/) to share knowledge on printer (in)security.
The highlights of the entire survey will be presented by Jens Müller for the first time at RuhrSec in Bochum.
The highlights of the entire survey will be presented by Jens Müller for the first time at RuhrSec in Bochum.
Background
There are many cool protocols and languages you can use to control your printer or your print jobs. We assume you have never heard of at least half of them. An overview is depicted in the following figure and described below.
Device control
This set of languages is used to control the printer device. With a device control language it is possible to retrieve the printer name or status. One of the most common languages is the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). SNMP is a UDP based protocol designed to manage various network components beyond printers as well, e.g. routers and servers.
Printing channel
The most common network printing protocols supported by printer devices are the Internet Printing Protocol (IPP), Line Printer Daemon (LPD), Server Message Block (SMB), and raw port 9100 printing. Each protocol has specific features like print job queue management or accounting. In our work, we used these protocols to transport malicious documents to the printers.Job control language
This is where it gets very interesting (for our attacks). A job control language manages printer settings like output trays or paper size. A de-facto standard for print job control is PJL. From a security perspective it is very useful that PJL is not limited to the current print job as some settings can be made permanent. It can further be used to change the printer's display or read/write files on the device.
Page description language
A page description language specifies the appearance of the actual document. One of the most common 'standard' page description languages is PostScript. While PostScript has lost popularity in desktop publishing and as a document exchange format (we use PDF now), it is still the preferred page description language for laser printers. PostScript is a stack-based, Turing-complete programming language consisting of about 400 instructions/operators. As a security aware researcher you probable know that some of them could be useful. Technically spoken, access to a PostScript interpreter can already be classified as code execution.
Attacks
Even though printers are an important attack target, security threats and scenarios for printers are discussed in very few research papers or technical reports. Our first step was therefore to perform a comprehensive analysis of all reported and published attacks in CVEs and security blogs. We then used this summary to systematize the known issues, to develop new attacks and to find a generic approach to apply them to different printers. We estimated that the best targets are the PostScript and PJL interpreters processing the actual print jobs since they can be exploited by a remote attacker with only the ability to 'print' documents, independent of the printing channel supported by the device.
We put the printer attacks into four categories.Denial-of-service (DoS)
Executing a DoS attack is as simple as sending these two lines of PostScript code to the printer which lead to the execution of an infinite loop:
Other attacks include:
- Offline mode. The PJL standard defines the OPMSG command which 'prompts the printer to display a specified message and go offline'.
- Physical damage. By continuously setting the long-term values for PJL variables, it is possible to physically destroy the printer's NVRAM which only survives a limited number of write cycles.
- Showpage redefinition. The PostScript 'showpage' operator is used in every document to print the page. An attacker can simply redefine this operator to do nothing.
Protection Bypass
Resetting a printer device to factory defaults is the best method to bypass protection mechanisms. This task is trivial for an attacker with local access to the printer, since all tested devices have documented procedures to perform a cold reset by pressing certain key combinations.
However, a factory reset can be performed also by a remote attacker, for example using SNMP if the device complies with RFC1759 (Printer MIB):
Other languages like HP's PML, Kyocera's PRESCRIBE or even PostScript offer similar functionalities.
Furthermore, our work shows techniques to bypass print job accounting on popular print servers like CUPS or LPRng.
However, a factory reset can be performed also by a remote attacker, for example using SNMP if the device complies with RFC1759 (Printer MIB):
Other languages like HP's PML, Kyocera's PRESCRIBE or even PostScript offer similar functionalities.
Furthermore, our work shows techniques to bypass print job accounting on popular print servers like CUPS or LPRng.
Print Job Manipulation
Some page description languages allow permanent modifications of themselves which leads to interesting attacks, like manipulating other users' print jobs. For example, it is possible to overlay arbitrary graphics on all further documents to be printed or even to replace text in them by redefining the 'showpage' and 'show' PostScript operators.
Information Disclosure
Printing over port 9100 provides a bidirectional channel, which can be used to leak sensitive information. For example, Brother based printers have a documented feature to read from or write to a certain NVRAM address using PJL:
Our prototype implementation simply increments this value to dump the whole NVRAM, which contains passwords for the printer itself but also for user-defined POP3/SMTP as well as for FTP and Active Directory profiles. This way an attacker can escalate her way into a network, using the printer device as a starting point.
Other attacks include:
Our prototype implementation simply increments this value to dump the whole NVRAM, which contains passwords for the printer itself but also for user-defined POP3/SMTP as well as for FTP and Active Directory profiles. This way an attacker can escalate her way into a network, using the printer device as a starting point.
Other attacks include:
- File system access. Both, the standards for PostScript and PJL specify functionality to access the printers file system. As it seems, some manufacturers have not limited this feature to a certain directory, which leads to the disclosure of sensitive information like passwords.
- Print job capture. If PostScript is used as a printer driver, printed documents can be captured. This is made possible by two interesting features of the PostScript language: First, permanently redefining operators allows an attacker to 'hook' into other users' print jobs and secondly, PostScript's capability to read its own code as data allows to easily store documents instead of executing them.
- Credential disclosure. PJL passwords, if set, can easily retrieved through brute-force attacks due to their limited key space (1..65535). PostScript passwords, on the other hand, can be cracked extremely fast (up to 100,000 password verifications per second) thanks to the performant PostScript interpreters.
PRET
To automate the introduced attacks, we wrote a prototype software entitled PRET. The main idea of PRET is to facilitate the communication between the end-user and the printer. Thus, by entering a UNIX-like command PRET translates it to PostScript or PJL, sends it to the printer, and evaluates the result. For example, PRET converts a UNIX command ls to the following PJL request:
It then collects the printer output and translates it to a user friendly output.
PRET implements the following list of commands for file system access on a printer device:
A proof-of-concept implementation demonstrating that advanced cross-site printing attacks are practical and a real-world threat to companies and institutions is available at http://hacking-printers.net/xsp/.
Our next post will be on adapting PostScript based attacks to websites.
Juraj Somorovsky
It then collects the printer output and translates it to a user friendly output.
Evaluation
As a highly motivated security researcher with a deep understanding of systematic analysis, you would probably obtain a list of about 20 - 30 well-used printers from the most important manufacturers, and perform an extensive security analysis using these printers.
However, this was not our case. To overcome the financial obstacles, we collected printers from various university chairs and facilities. While our actual goal was to assemble a pool of printers containing at least one model for each of the top ten manufacturers, we practically took what we could get. The result is depicted in the following figure:
The assembled devices were not brand-new anymore and some of them were not even completely functional. Three printers had physically broken printing functionality so it was not possible to evaluate all the presented attacks. Nevertheless, these devices represent a good mix of printers used in a typical university or office environment.
Before performing the attacks, we of course installed the newest firmware on each of the devices. The results of our evaluation show that we could find multiple attacks against each printer. For example, simple DoS attacks with malicious PostScript files containing infinite loops are applicable to each printer. Only the HP LaserJet M2727nf had a watchdog mechanism and restarted itself after about ten minutes. Physical damage could be caused to about half of the tested device within 24 hours of NVRAM stressing. For a majority of devices, print jobs could be manipulated or captured.
PostScript, PJL and PML based attacks can even be exploited by a web attacker using advanced cross-site printing techniques. In the scope of our research, we discovered a novel approach – 'CORS spoofing' – to leak information like captured print jobs from a printer device given only a victim's browser as carrier.However, this was not our case. To overcome the financial obstacles, we collected printers from various university chairs and facilities. While our actual goal was to assemble a pool of printers containing at least one model for each of the top ten manufacturers, we practically took what we could get. The result is depicted in the following figure:
The assembled devices were not brand-new anymore and some of them were not even completely functional. Three printers had physically broken printing functionality so it was not possible to evaluate all the presented attacks. Nevertheless, these devices represent a good mix of printers used in a typical university or office environment.
A proof-of-concept implementation demonstrating that advanced cross-site printing attacks are practical and a real-world threat to companies and institutions is available at http://hacking-printers.net/xsp/.
Our next post will be on adapting PostScript based attacks to websites.
Authors of this Post
Jens MüllerJuraj Somorovsky
Vladislav Mladenov
Continue reading
Ophcrack
 " Ophcrack is an open source (GPL license) program that cracks Windows LM hashes using rainbow tables. The program includes the ability to import the hashes from a variety of formats, including dumping directly from the SAM files of Windows. There is also a Live CD version which automates the retrieval, decryption, and cracking of passwords from a Windows system. Rainbow tables for LM hashes of alphanumeric passwords are provided for free by the developers. These tables can crack 99.9% of alphanumeric passwords of up to 14 characters in usually a few seconds, and at most a few minutes. Larger rainbow tables (for LM hashes of passwords with all printable characters, including symbols and space) are available for purchase from Objectif Securité. Starting with version 2.3, Ophcrack also cracks NT hashes. This is necessary if generation of the LM hash is disabled (this is default on Windows Vista), or if the password is longer than 14 characters (in which case the LM hash is not stored)." read more...
" Ophcrack is an open source (GPL license) program that cracks Windows LM hashes using rainbow tables. The program includes the ability to import the hashes from a variety of formats, including dumping directly from the SAM files of Windows. There is also a Live CD version which automates the retrieval, decryption, and cracking of passwords from a Windows system. Rainbow tables for LM hashes of alphanumeric passwords are provided for free by the developers. These tables can crack 99.9% of alphanumeric passwords of up to 14 characters in usually a few seconds, and at most a few minutes. Larger rainbow tables (for LM hashes of passwords with all printable characters, including symbols and space) are available for purchase from Objectif Securité. Starting with version 2.3, Ophcrack also cracks NT hashes. This is necessary if generation of the LM hash is disabled (this is default on Windows Vista), or if the password is longer than 14 characters (in which case the LM hash is not stored)." read more...Website: http://ophcrack.sourceforge.net
Read more
Wednesday, June 10, 2020
CEH: System Hacking, Cracking A Password, Understanding The LAN Manager Hash, NetBIOS DoS Attacks
Passwords are the key element of information require to access the system. Similarly, the first step is to access the system is that you should know how to crack the password of the target system. There is a fact that users selects passwords that are easy to guess. Once a password is guessed or cracked, it can be the launching point for escalating privileges, executing applications, hiding files, and covering tracks. If guessing a password fails, then passwords may be cracked manually or with automated tools such as a dictionary or brute-force method.
Cracking a Password
Passwords are stored in the Security Accounts Manager (SAM) file on a Windows system and in a password shadow file on a Linux system.
Manual password cracking involves attempting to log on with different passwords. The hacker follows these steps:
- Find a valid user account (such as Administrator or Guest).
- Create a list of possible passwords.
- Rank the passwords from high to low probability.
- Key in each password.
- Try again until a successful password is found.
A more efficient way of cracking a password is to gain access to the password file on a system. Most systems hash (one-way encrypt) a password for storage on a system. During the logon process, the password entered by the user is hashed using the same algorithm and then compared to the hashed passwords stored in the file. A hacker can attempt to gain access to the hashing algorithm stored on the server instead of trying to guess or otherwise identify the password. If the hacker is successful, they can decrypt the passwords stored on the server.
Understanding the LAN Manager Hash
Windows 2000 uses NT LAN Manager (NTLM) hashing to secure passwords in transit on the network. Depending on the password, NTLM hashing can be weak and easy to break. For example, let's say that the password is 123456abcdef . When this password is encrypted with the NTLM algorithm, it's first converted to all uppercase: 123456ABCDEF . The password is padded with null (blank) characters to make it 14 characters long: 123456ABCDEF__ . Before the password is encrypted, the 14-character string is split in half: 123456A andBCDEF__ . Each string is individually encrypted, and the results are concatenated:
123456A = 6BF11E04AFAB197F
BCDEF__ = F1E9FFDCC75575B15
The hash is 6BF11E04AFAB197FF1E9FFDCC75575B15 .
Cracking Windows 2000 Passwords
The SAM file in Windows contains the usernames and hashed passwords. It's located in the Windows\system32\config directory. The file is locked when the operating system is running so that a hacker can't attempt to copy the file while the machine is booted to Windows.One option for copying the SAM file is to boot to an alternate operating system such as DOS or Linux with a boot CD. Alternately, the file can be copied from the repair directory. If a system administrator uses the RDISK feature of Windows to back up the system, then a compressed copy of the SAM file called SAM._ is created in C:\windows\repair . To expand this file, use the following command at the command prompt:
C:\>expand sam._ sam
After the file is uncompressed, a dictionary, hybrid, or brute-force attack can be run against the SAM file using a tool like L0phtCrack. A similar tool to L0phtcrack is Ophcrack.
Download and install ophcrack from http://ophcrack.sourceforge.net/
Redirecting the SMB Logon to the Attacker
Another way to discover passwords on a network is to redirect the Server Message Block (SMB) logon to an attacker's computer so that the passwords are sent to the hacker. In order to do this, the hacker must sniff the NTLM responses from the authentication server and trick the victim into attempting Windows authentication with the attacker's computer.A common technique is to send the victim an email message with an embedded link to a fraudulent SMB server. When the link is clicked, the user unwittingly sends their credentials over the network.
SMBRelay
An SMB server that captures usernames and password hashes from incomingSMB traffic. SMBRelay can also perform man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
SMBRelay2
Similar to SMBRelay but uses NetBIOS names instead of IP addresses to capture usernames and passwords.pwdump2
A program that extracts the password hashes from a SAM file on a Windows system. The extracted password hashes can then be run through L0phtCrack to break the passwords.Samdump
Another program that extracts NTLM hashed passwords from a SAM file.C2MYAZZ
A spyware program that makes Windows clients send their passwords as clear text. It displays usernames and their passwords as users attach to server resources.NetBIOS DoS Attacks
A NetBIOS denial-of-service (DoS) attack sends a NetBIOS Name Release message to the NetBIOS Name Service on a target Windows systems and forces the system to place its name in conflict so that the name can no longer be used. This essentially blocks the client from participating in the NetBIOS network and creates a network DoS for that system.- Start with a memorable phrase, such as "Maryhadalittlelamb"
- Change every other character to uppercase, resulting in "MaRyHaDaLiTtLeLaMb"
- Change a to @ and i to 1 to yield "M@RyH@D@L1TtLeL@Mb"
- Drop every other pair to result in a secure repeatable password or "M@H@L1LeMb"
Now you have a password that meets all the requirements, yet can be "remade" if necessary.
More articles
OpenVAS
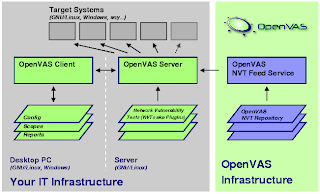 "OpenVAS stands for Open Vulnerability Assessment System and is a network security scanner with associated tools like a graphical user front-end. The core is a server component with a set of network vulnerability tests (NVTs) to detect security problems in remote systems and applications." read more...
"OpenVAS stands for Open Vulnerability Assessment System and is a network security scanner with associated tools like a graphical user front-end. The core is a server component with a set of network vulnerability tests (NVTs) to detect security problems in remote systems and applications." read more...More articles
July 2019 Connector
*|MC_PREVIEW_TEXT|*
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Blog Archive
-
►
2025
(47)
- ► 06/29 - 07/06 (2)
- ► 06/01 - 06/08 (1)
- ► 05/25 - 06/01 (1)
- ► 04/27 - 05/04 (1)
- ► 04/13 - 04/20 (2)
- ► 03/23 - 03/30 (6)
- ► 03/16 - 03/23 (1)
- ► 02/16 - 02/23 (2)
- ► 02/09 - 02/16 (2)
- ► 02/02 - 02/09 (1)
- ► 01/26 - 02/02 (2)
- ► 01/19 - 01/26 (3)
- ► 01/12 - 01/19 (5)
- ► 01/05 - 01/12 (18)
-
►
2024
(53)
- ► 12/22 - 12/29 (1)
- ► 11/10 - 11/17 (1)
- ► 09/22 - 09/29 (1)
- ► 03/03 - 03/10 (1)
- ► 02/04 - 02/11 (2)
- ► 01/28 - 02/04 (9)
- ► 01/21 - 01/28 (27)
- ► 01/14 - 01/21 (11)
-
►
2023
(62)
- ► 12/31 - 01/07 (1)
- ► 12/03 - 12/10 (1)
- ► 09/24 - 10/01 (1)
- ► 08/13 - 08/20 (1)
- ► 08/06 - 08/13 (2)
- ► 07/30 - 08/06 (3)
- ► 07/23 - 07/30 (2)
- ► 07/09 - 07/16 (1)
- ► 06/11 - 06/18 (5)
- ► 06/04 - 06/11 (10)
- ► 05/28 - 06/04 (23)
- ► 05/21 - 05/28 (12)
-
►
2022
(1)
- ► 07/31 - 08/07 (1)
-
▼
2020
(357)
- ► 09/20 - 09/27 (2)
- ► 09/06 - 09/13 (2)
- ► 08/30 - 09/06 (5)
- ► 08/23 - 08/30 (19)
- ► 08/16 - 08/23 (26)
- ► 08/09 - 08/16 (23)
- ► 08/02 - 08/09 (23)
- ► 07/26 - 08/02 (23)
- ► 07/19 - 07/26 (23)
- ► 07/12 - 07/19 (23)
- ► 07/05 - 07/12 (23)
- ► 06/28 - 07/05 (15)
-
▼
06/07 - 06/14
(15)
- Galileo - Web Application Audit Framework
- HOW TO BOOST UP BROWSING SPEED?
- BurpSuite Introduction & Installation
- Printer Security
- Ophcrack
- CEH: System Hacking, Cracking A Password, Understa...
- OpenVAS
- Freefloat FTP Server 1.0 | Remote Buffer Overflow ...
- July 2019 Connector
- Potao Express Samples
- Reversing C++ String And QString
- System Hacking: Password Cracking Techniques And T...
- PHoss: A Password Sniffer
- Files Download Information
- PortWitness - Tool For Checking Whether A Domain O...
- ► 05/31 - 06/07 (12)
- ► 05/17 - 05/24 (22)
- ► 05/10 - 05/17 (16)
- ► 05/03 - 05/10 (7)
- ► 04/26 - 05/03 (7)
- ► 04/19 - 04/26 (19)
- ► 04/12 - 04/19 (26)
- ► 04/05 - 04/12 (2)
- ► 03/22 - 03/29 (4)
- ► 03/15 - 03/22 (6)
- ► 03/01 - 03/08 (5)
- ► 02/23 - 03/01 (2)
- ► 02/16 - 02/23 (6)
- ► 02/09 - 02/16 (1)
-
►
2019
(1072)
- ► 12/01 - 12/08 (12)
- ► 11/24 - 12/01 (38)
- ► 11/17 - 11/24 (24)
- ► 09/15 - 09/22 (54)
- ► 09/08 - 09/15 (82)
- ► 09/01 - 09/08 (52)
- ► 08/25 - 09/01 (56)
- ► 08/18 - 08/25 (68)
- ► 08/11 - 08/18 (66)
- ► 08/04 - 08/11 (62)
- ► 07/28 - 08/04 (61)
- ► 07/21 - 07/28 (64)
- ► 07/14 - 07/21 (71)
- ► 07/07 - 07/14 (65)
- ► 06/30 - 07/07 (60)
- ► 06/23 - 06/30 (37)
- ► 06/16 - 06/23 (26)
- ► 06/09 - 06/16 (52)
- ► 06/02 - 06/09 (48)
- ► 05/26 - 06/02 (50)
- ► 05/19 - 05/26 (9)
- ► 03/31 - 04/07 (3)
- ► 03/24 - 03/31 (11)
- ► 03/17 - 03/24 (1)
-
►
2018
(2)
- ► 06/24 - 07/01 (2)
-
►
2015
(1)
- ► 03/15 - 03/22 (1)
-
►
2012
(3)
- ► 03/11 - 03/18 (1)
- ► 01/29 - 02/05 (1)
- ► 01/08 - 01/15 (1)
-
►
2011
(38)
- ► 10/23 - 10/30 (1)
- ► 10/16 - 10/23 (1)
- ► 10/09 - 10/16 (1)
- ► 10/02 - 10/09 (4)
- ► 09/25 - 10/02 (2)
- ► 09/18 - 09/25 (2)
- ► 05/29 - 06/05 (1)
- ► 05/22 - 05/29 (1)
- ► 05/15 - 05/22 (2)
- ► 05/08 - 05/15 (2)
- ► 04/10 - 04/17 (2)
- ► 04/03 - 04/10 (1)
- ► 03/27 - 04/03 (1)
- ► 03/20 - 03/27 (3)
- ► 03/06 - 03/13 (2)
- ► 02/27 - 03/06 (3)
- ► 02/13 - 02/20 (1)
- ► 02/06 - 02/13 (1)
- ► 01/23 - 01/30 (1)
- ► 01/16 - 01/23 (1)
- ► 01/09 - 01/16 (3)
- ► 01/02 - 01/09 (2)
-
►
2010
(61)
- ► 12/05 - 12/12 (2)
- ► 11/28 - 12/05 (2)
- ► 11/14 - 11/21 (2)
- ► 11/07 - 11/14 (3)
- ► 10/31 - 11/07 (5)
- ► 10/24 - 10/31 (5)
- ► 10/17 - 10/24 (4)
- ► 05/16 - 05/23 (1)
- ► 05/02 - 05/09 (2)
- ► 04/18 - 04/25 (3)
- ► 04/11 - 04/18 (2)
- ► 03/21 - 03/28 (4)
- ► 03/14 - 03/21 (3)
- ► 03/07 - 03/14 (4)
- ► 02/28 - 03/07 (1)
- ► 02/21 - 02/28 (2)
- ► 02/07 - 02/14 (2)
- ► 01/31 - 02/07 (2)
- ► 01/24 - 01/31 (3)
- ► 01/17 - 01/24 (2)
- ► 01/10 - 01/17 (3)
- ► 01/03 - 01/10 (4)
-
►
2009
(3)
- ► 12/13 - 12/20 (3)


















